Introduction
The human body is a complex system that relies on various chemicals and compounds to maintain optimal health. One such compound is uric acid, a byproduct of the metabolic breakdown of purines, which are naturally occurring substances found in foods and body tissues.
Uric acid plays a crucial role in the body’s antioxidant defense system, protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. However, when uric acid levels become imbalanced, it can lead to health issues such as gout, kidney stones, and chronic kidney disease.
Brief explanation of uric acid and its role in the body
Uric acid is a waste product that results from the breakdown of purines during digestion. Purines are found in various foods like seafood, organ meats (such as liver and kidneys), red meat, some vegetables (like mushrooms and spinach), and certain beverages like beer. Normally, uric acid dissolves in our blood and gets excreted through urine without causing any harm.
However, when there is an excess production or inadequate elimination of uric acid from the body, it can accumulate in joints or form crystals in the kidneys. The build-up of uric acid crystals can lead to inflammatory conditions like gout.
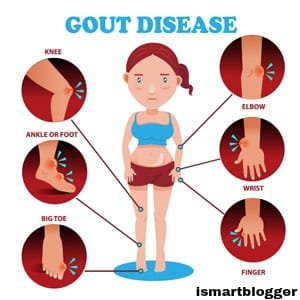
Gout typically affects joints—most commonly the big toe—but can also affect other joints such as ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, or fingers. The inflammation causes severe pain and swelling making mobility challenging for affected individuals.

Importance of maintaining healthy uric acid levels
Maintaining healthy levels of uric acid is paramount for overall well-being as imbalances can have detrimental effects on our health. High levels of uric acid increase the risk of developing various health conditions including gouty arthritis—a painful form of arthritis—where crystals form within joints leading to inflammation. Moreover
Understanding Uric Acid and its Causes
An Atomic Insight into Uric Acid
Uric acid, a chemical compound derived from the breakdown of purines in our bodies, plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of antioxidants and free radicals. It is created through the natural breakdown of purine nucleotides, which are components of DNA and RNA.
As these nucleotides are broken down, they produce uric acid as a waste product. This acid is then transported to the kidneys where it is dissolved in urine and eventually eliminated from the body.
The Culprits Behind Elevated Uric Acid Levels
Several factors can contribute to heightened levels of uric acid, often leading to hyperuricemia – a condition marked by excessive amounts of uric acid in the bloodstream. The primary culprits are diet, lifestyle choices, and genetic predisposition.
Dietary habits significantly impact uric acid production. Foods high in purines such as organ meats (e.g., liver and kidneys), shellfish (e.g., mussels and scallops), and certain alcoholic beverages (especially beer) have been linked to increased levels of uric acid.
When consumed excessively, these foods overwhelm our bodies’ ability to metabolize purines effectively. Lifestyle choices also play a significant role in determining uric acid levels.
Obesity, sedentary behavior, excessive alcohol consumption – particularly beer – can contribute to elevated levels of this compound. Additionally, dehydration can hinder the kidneys’ ability to efficiently remove uric acid from circulation.
Unmasking Gout’s Connection with High Uric Acid
Gout, an excruciating form of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe joint inflammation primarily affecting the big toe but potentially affecting other joints too, has an intimate relationship with elevated uric acid levels. In individuals with hyperuricemia, uric acid can accumulate and crystallize in the joints, leading to the hallmark symptoms of gout.
When uric acid crystals precipitate within the joint space, they incite an immune response that triggers inflammation and intense pain. The affected joint becomes swollen, hot, and tender.
These painful gout attacks can last for days or even weeks. Without proper management of uric acid levels, recurrent gout flares are likely to occur.
The Stealthy Link Between Kidney Stones and Uric Acid
In addition to its association with gout, high levels of uric acid can also contribute to the formation of kidney stones – small, hard deposits that develop in the kidneys or urinary tract. When excessive amounts of uric acid accumulate in urine due to hyperuricosuria (excessively high urinary uric acid levels), they can crystallize and form kidney stones. These sharp crystals can cause excruciating pain as they pass through the urinary system.
The size and location of these stones determine the intensity of pain experienced by those affected. It is important for individuals prone to kidney stone formation or those with a history of kidney stones to regulate their uric acid levels effectively.
Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind uric acid production and recognizing its various causes is essential for developing effective strategies to lower its concentration naturally. By addressing diet choices, lifestyle habits, and genetic predisposition while understanding how hyperuricemia relates to conditions like gout and kidney stones, one moves closer towards achieving optimal health outcomes.
Dietary Changes to Lower Uric Acid
Importance of a Balanced Diet for Managing Uric Acid Levels
Maintaining a well-balanced diet is crucial in managing uric acid levels. By consuming the right foods and avoiding those that contribute to purine buildup, individuals can effectively lower their uric acid levels and reduce the risk of associated health issues like gout. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients while minimizing triggers for excess uric acid production.
Foods to Avoid that are High in Purines
Certain foods are high in purines, compounds that break down into uric acid during digestion. It is advisable to limit or avoid these purine-rich foods to manage uric acid levels effectively. Organ meats such as liver, kidneys, and sweetbreads are particularly high in purines and should be avoided or consumed sparingly.
Shellfish like mussels, scallops, and anchovies also contain significant amounts of purines. Additionally, alcoholic beverages like beer are known culprits for elevating uric acid levels.
Explanation of Purines and their Role in Increasing Uric Acid Production
Purines are natural substances found in many food items and also produced by our bodies as part of normal cell metabolism. When we consume foods rich in purines, they break down into uric acid as part of the digestive process.
Excessive consumption of high-purine foods can lead to an accumulation of uric acid beyond what our bodies can effectively excrete through urine. The buildup of excess uric acid often results in hyperuricemia—a condition characterized by elevated levels of uric acid—leading to various health problems such as gouty arthritis.
Alternative Protein Sources Low in Purines
While it is important to reduce consumption of high-purine protein sources, it does not mean eliminating protein altogether. Lean meats like chicken, turkey, and lean cuts of beef are excellent alternatives as they contain lower purine content.
For those following a vegetarian or vegan diet, tofu and other soy-based products provide a good source of low-purine proteins. Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are also fantastic options rich in protein but with minimal purine content.
Emphasizing the Consumption of Fruits and Vegetables Rich in Antioxidants
Incorporating fruits and vegetables into one’s diet is not only beneficial for overall health but also effective in reducing uric acid levels naturally. Many fruits and veggies possess antioxidant properties that help neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation—the root cause of uric acid buildup.
Berries like strawberries, blueberries, and cherries have been found to have anti-inflammatory effects and aid in lowering uric acid levels. Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are highly recommended due to their high vitamin C content—vitamin C has been shown to reduce uric acid production.
Specific Fruits with Anti-inflammatory Properties
Certain fruits stand out for their exceptional anti-inflammatory properties that specifically target uric acid reduction. Tart cherries have gained considerable attention for their ability to lower uric acid levels significantly.
Pineapple contains bromelain—an enzyme known to reduce inflammation—making it an excellent addition to the diet for managing uric acid-related conditions like gout. Moreover, consuming apples regularly has been associated with decreased serum uric acid levels.
The Benefits of Incorporating Leafy Greens into the Diet
Leafy greens offer numerous health benefits while aiding in reducing excess uric acid levels naturally. Vegetables like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are rich sources of essential nutrients such as vitamins A, C, and K, as well as minerals like magnesium and calcium.
These nutrients contribute to overall health and have been shown to help regulate uric acid metabolism. Additionally, their alkalizing properties can help neutralize excess acid in the body, promoting a healthy acid-base balance and aiding in uric acid regulation.
By making dietary adjustments that prioritize a balanced intake of low-purine proteins, antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables, particularly those with anti-inflammatory properties like tart cherries and pineapples, as well as leafy greens packed with essential nutrients, individuals can effectively lower uric acid levels. Implementing these dietary changes not only helps manage conditions associated with high uric acid such as gout but also promotes overall health and well-being.
Hydration for Uric Acid Control
The importance of staying hydrated for overall health
Proper hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal health, and it plays a significant role in controlling uric acid levels. Water is essential for various bodily functions, including digestion, circulation, and the elimination of waste products.
By staying adequately hydrated, you can support the efficient functioning of your kidneys, which are responsible for filtering and excreting uric acid from the body. Furthermore, proper hydration helps prevent dehydration-related conditions such as kidney stones that can be triggered by elevated uric acid levels.
Explanation on how drinking plenty of water can help flush out excess uric acid from the body
When you consume an adequate amount of water regularly, it helps dilute your urine and promotes increased urine output. As a consequence, more uric acid is excreted through urine rather than being retained in the body.
Water acts as a natural diuretic by stimulating kidney function and enhancing urine production. This increased volume aids in flushing out excess uric acid from your system and reducing its concentration in the bloodstream.
Additionally, proper hydration prevents uric acid crystals from forming or accumulating in joints, which is often associated with painful conditions like gout. When you consume sufficient water throughout the day, it minimizes the risk of these crystals depositing in joints by promoting their dissolution and subsequent elimination through urine.
Tips on increasing water intake throughout the day
To ensure adequate hydration and control uric acid levels effectively: 1. Drink at least 8-10 cups (64-80 ounces) of water daily. 2. Carry a reusable water bottle with you to encourage regular sipping throughout the day.
3. Set reminders on your phone or use apps to track your water consumption. 4. Include herbal teas or infused water for variety while avoiding sugary beverages.
5. Eat water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges. 6. Consider drinking a glass of water before each meal to help meet your daily intake goals.
7. Limit the consumption of alcohol and caffeinated beverages, as they can contribute to dehydration. Remember, individual hydration needs may vary based on factors like age, weight, activity level, climate conditions, and certain health conditions.
It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized recommendations on water intake. By prioritizing proper hydration through regular water consumption and adopting these tips, you can support your body’s natural mechanisms for regulating uric acid levels and promote overall well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications for Uric Acid Reduction
Regular exercise as a means to control weight gain which can contribute to higher uric acid levels
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and managing uric acid levels. One of the primary benefits of exercise is its ability to help control weight gain, which is closely linked to elevated uric acid levels.
Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, leading to increased production of uric acid. By engaging in regular exercise, individuals can effectively manage their weight and reduce the risk of developing conditions associated with high uric acid, such as gout.
Types of exercises that facilitate uric acid reduction
When it comes to choosing the right exercises for lowering uric acid naturally, it is essential to focus on activities that promote cardiovascular fitness and strengthen the muscles without putting excessive strain on the joints. Low-impact exercises are highly recommended for individuals with elevated uric acid levels.
Swimming, brisk walking, cycling, and yoga are excellent options that provide numerous health benefits while minimizing joint stress. Incorporating resistance training into the exercise routine can also be beneficial for reducing uric acid levels.
Strength training exercises using weights or resistance bands help increase muscle mass and improve metabolic rate. This contributes to better overall body composition and aids in weight management.
Conclusion
Adopting certain lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to reducing uric acid naturally and improving overall health outcomes. Regular exercise not only helps control weight gain but also strengthens muscles, enhances cardiovascular fitness, and promotes overall well-being. Engaging in low-impact activities like swimming or brisk walking combined with resistance training can provide an effective approach towards lowering uric acid levels.
By making dietary changes such as avoiding purine-rich foods and emphasizing antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables along with staying adequately hydrated through increased water intake, individuals can further support the natural reduction of uric acid levels. It is important to remember that these lifestyle modifications should be incorporated in consultation with a healthcare professional, particularly for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. With commitment and dedication to a healthier lifestyle, it is possible to manage uric acid levels effectively and reduce the risk of developing complications associated with high uric acid. By taking control of one’s diet, exercise routine, and overall well-being, individuals can pave the way towards a life free from the burdens of elevated uric acid levels.